[HOME PAGE] [STORES] [CLASSICISTRANIERI.COM] [FOTO] [YOUTUBE CHANNEL]
 |  |  |
| | ||
Medical Encyclopedia |
|
| Other encyclopedia topics: | A-Ag Ah-Ap Aq-Az B-Bk Bl-Bz C-Cg Ch-Co Cp-Cz D-Di Dj-Dz E-Ep Eq-Ez F G H-Hf Hg-Hz I-In Io-Iz J K L-Ln Lo-Lz M-Mf Mg-Mz N O P-Pl Pm-Pz Q R S-Sh Si-Sp Sq-Sz T-Tn To-Tz U V W X Y Z 0-9 |
Polyarteritis nodosa
| Contents of this page: | |
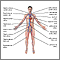
Illustrations
Click on the following link to visit or download this HTML page
|
Click on the following link to visit or download this HTML page
|
Click on the following link to visit or download this HTML page
|
Click on the following link to visit or download this HTML page
|
Alternative Names Return to top
Periarteritis nodosaDefinition Return to top
Polyarteritis nodosa is a serious blood vessel disease in which small and medium-sized arteries become swollen and damaged.
Causes Return to top
Polyarteritis nodosa is a disease of unknown cause that affects arteries, the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to organs and tissues. It occurs when certain immune cells attack the affected arteries.
More adults than children get this disease. It damages the tissues supplied by the affected arteries because the tissues aren't receiving the oxygen and nourishment they need.
In this disease, symptoms result from damage to affected organs, often the skin, heart, kidneys, and nervous system.
Generalized symptoms include fever, fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, and weight loss. Muscle and joint aches are common. The skin may show rashes, swelling, ulcers, and lumps.
Nerve involvement may cause sensory changes with numbness, pain, burning, and weakness. Central nervous system involvement may cause strokes or seizures. Kidney involvement can produce varying degrees of renal (kidney) failure.
When heart arteries are involved, heart attack, heart failure, and inflammation of the sack around the heart (pericarditis) can occur.
Symptoms Return to top
Exams and Tests Return to top
There are no specific lab tests for diagnosing polyarteritis nodosa. Diagnosis is based on the physical examination and a few laboratory studies that help to confirm the diagnosis:
- CBC may show a higher-than-normal white blood count.
- ESR or CRP is often higher than normal.
- Tissue biopsy reveals inflammation in small arteries, called arteritis.
- Immunoglobulins may be increased.
Treatment Return to top
Treatment involves medications to suppress the immune system, including prednisone and cyclophosphamide.
Outlook (Prognosis) Return to top
Current treatments using steroids and other drugs that suppress the immune system (such as cyclophosphamide) can improve symptoms and the chance of long-term survival. The most serious associated conditions generally involve the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract. Without treatment, the outlook is poor.
Possible Complications Return to top
- Heart attack
- Intestinal necrosis and perforation
- Kidney failure
- Stroke
When to Contact a Medical Professional Return to top
Call your health care provider if you develop symptoms of this disorder. Early diagnosis and treatment may improve the chance of a good outcome.
Prevention Return to top
There is no known prevention. However, early treatment can prevent some damage and symptoms.
References Return to top
Sergent JS. Polyarteritis and Related Disorders. In: Harris ED Jr., Budd RC, Genovese MC, Firestein GS, Sargent JS, eds. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2005: chap 84.
Stone JH. The Systemic Vasculitides. In: Goldman L, Ausiello D, eds. Cecil Medicine. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2007: chap 291.
Update Date: 7/24/2008 Updated by: Neil J. Gonter, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Columbia University, New York, NY, and private practice specializing in Rheumatology at Rheumatology Associates of North Jersey, Teaneck, NJ. Review provided by Verimed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, A.D.A.M., Inc.

The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 1997-2009, A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
EDIZIONI DI PUBBLICO DOMINIO (HTML)
- Alighieri - La Divina Commedia
RISORSE DAL WEB:
Encyclopaedia Britannica 1911 - PDF
Project Gutenberg: DVD-ROM 2007
Wikipedia for Schools - ENGLISH
Wikipedia for Schools - FRENCH
Wikipedia for Schools - SPANISH
Wikipedia for Schools - PORTUGUESE
Static Wikipedia
(no
images)
aa
- ab
- af
- ak
- als
- am
- an
- ang
- ar
- arc
- as
- ast
- av
- ay
- az
- ba
- bar
- bat_smg
- bcl
- be
- be_x_old
- bg
- bh
- bi
- bm
- bn
- bo
- bpy
- br
- bs
- bug
- bxr
- ca
- cbk_zam
- cdo
- ce
- ceb
- ch
- cho
- chr
- chy
- co
- cr
- crh
- cs
- csb
- cu
- cv
- cy
- da
- de
- diq
- dsb
- dv
- dz
- ee
- el
- eml
- en
- eo
- es
- et
- eu
- ext
- fa
- ff
- fi
- fiu_vro
- fj
- fo
- fr
- frp
- fur
- fy
- ga
- gan
- gd
- gl
- glk
- gn
- got
- gu
- gv
- ha
- hak
- haw
- he
- hi
- hif
- ho
- hr
- hsb
- ht
- hu
- hy
- hz
- ia
- id
- ie
- ig
- ii
- ik
- ilo
- io
- is
- it
- iu
- ja
- jbo
- jv
- ka
- kaa
- kab
- kg
- ki
- kj
- kk
- kl
- km
- kn
- ko
- kr
- ks
- ksh
- ku
- kv
- kw
- ky
- la
- lad
- lb
- lbe
- lg
- li
- lij
- lmo
- ln
- lo
- lt
- lv
- map_bms
- mdf
- mg
- mh
- mi
- mk
- ml
- mn
- mo
- mr
- mt
- mus
- my
- myv
- mzn
- na
- nah
- nap
- nds
- nds_nl
- ne
- new
- ng
- nl
- nn
- no
- nov
- nrm
- nv
- ny
- oc
- om
- or
- os
- pa
- pag
- pam
- pap
- pdc
- pi
- pih
- pl
- pms
- ps
- pt
- qu
- quality
- rm
- rmy
- rn
- ro
- roa_rup
- roa_tara
- ru
- rw
- sa
- sah
- sc
- scn
- sco
- sd
- se
- sg
- sh
- si
- simple
- sk
- sl
- sm
- sn
- so
- sr
- srn
- ss
- st
- stq
- su
- sv
- sw
- szl
- ta
- te
- tet
- tg
- th
- ti
- tk
- tl
- tlh
- tn
- to
- tpi
- tr
- ts
- tt
- tum
- tw
- ty
- udm
- ug
- uk
- ur
- uz
- ve
- vec
- vi
- vls
- vo
- wa
- war
- wo
- wuu
- xal
- xh
- yi
- yo
- za
- zea
- zh
- zh_classical
- zh_min_nan
- zh_yue
- zu
-
Static Wikipedia 2007 (no
images)
aa
- ab
- af
- ak
- als
- am
- an
- ang
- ar
- arc
- as
- ast
- av
- ay
- az
- ba
- bar
- bat_smg
- bcl
- be
- be_x_old
- bg
- bh
- bi
- bm
- bn
- bo
- bpy
- br
- bs
- bug
- bxr
- ca
- cbk_zam
- cdo
- ce
- ceb
- ch
- cho
- chr
- chy
- co
- cr
- crh
- cs
- csb
- cu
- cv
- cy
- da
- de
- diq
- dsb
- dv
- dz
- ee
- el
- eml
- en
- eo
- es
- et
- eu
- ext
- fa
- ff
- fi
- fiu_vro
- fj
- fo
- fr
- frp
- fur
- fy
- ga
- gan
- gd
- gl
- glk
- gn
- got
- gu
- gv
- ha
- hak
- haw
- he
- hi
- hif
- ho
- hr
- hsb
- ht
- hu
- hy
- hz
- ia
- id
- ie
- ig
- ii
- ik
- ilo
- io
- is
- it
- iu
- ja
- jbo
- jv
- ka
- kaa
- kab
- kg
- ki
- kj
- kk
- kl
- km
- kn
- ko
- kr
- ks
- ksh
- ku
- kv
- kw
- ky
- la
- lad
- lb
- lbe
- lg
- li
- lij
- lmo
- ln
- lo
- lt
- lv
- map_bms
- mdf
- mg
- mh
- mi
- mk
- ml
- mn
- mo
- mr
- mt
- mus
- my
- myv
- mzn
- na
- nah
- nap
- nds
- nds_nl
- ne
- new
- ng
- nl
- nn
- no
- nov
- nrm
- nv
- ny
- oc
- om
- or
- os
- pa
- pag
- pam
- pap
- pdc
- pi
- pih
- pl
- pms
- ps
- pt
- qu
- quality
- rm
- rmy
- rn
- ro
- roa_rup
- roa_tara
- ru
- rw
- sa
- sah
- sc
- scn
- sco
- sd
- se
- sg
- sh
- si
- simple
- sk
- sl
- sm
- sn
- so
- sr
- srn
- ss
- st
- stq
- su
- sv
- sw
- szl
- ta
- te
- tet
- tg
- th
- ti
- tk
- tl
- tlh
- tn
- to
- tpi
- tr
- ts
- tt
- tum
- tw
- ty
- udm
- ug
- uk
- ur
- uz
- ve
- vec
- vi
- vls
- vo
- wa
- war
- wo
- wuu
- xal
- xh
- yi
- yo
- za
- zea
- zh
- zh_classical
- zh_min_nan
- zh_yue
- zu
-
Static Wikipedia 2006 (no
images)
aa
- ab
- af
- ak
- als
- am
- an
- ang
- ar
- arc
- as
- ast
- av
- ay
- az
- ba
- bar
- bat_smg
- bcl
- be
- be_x_old
- bg
- bh
- bi
- bm
- bn
- bo
- bpy
- br
- bs
- bug
- bxr
- ca
- cbk_zam
- cdo
- ce
- ceb
- ch
- cho
- chr
- chy
- co
- cr
- crh
- cs
- csb
- cu
- cv
- cy
- da
- de
- diq
- dsb
- dv
- dz
- ee
- el
- eml
- eo
- es
- et
- eu
- ext
- fa
- ff
- fi
- fiu_vro
- fj
- fo
- fr
- frp
- fur
- fy
- ga
- gan
- gd
- gl
- glk
- gn
- got
- gu
- gv
- ha
- hak
- haw
- he
- hi
- hif
- ho
- hr
- hsb
- ht
- hu
- hy
- hz
- ia
- id
- ie
- ig
- ii
- ik
- ilo
- io
- is
- it
- iu
- ja
- jbo
- jv
- ka
- kaa
- kab
- kg
- ki
- kj
- kk
- kl
- km
- kn
- ko
- kr
- ks
- ksh
- ku
- kv
- kw
- ky
- la
- lad
- lb
- lbe
- lg
- li
- lij
- lmo
- ln
- lo
- lt
- lv
- map_bms
- mdf
- mg
- mh
- mi
- mk
- ml
- mn
- mo
- mr
- mt
- mus
- my
- myv
- mzn
- na
- nah
- nap
- nds
- nds_nl
- ne
- new
- ng
- nl
- nn
- no
- nov
- nrm
- nv
- ny
- oc
- om
- or
- os
- pa
- pag
- pam
- pap
- pdc
- pi
- pih
- pl
- pms
- ps
- pt
- qu
- quality
- rm
- rmy
- rn
- ro
- roa_rup
- roa_tara
- ru
- rw
- sa
- sah
- sc
- scn
- sco
- sd
- se
- sg
- sh
- si
- simple
- sk
- sl
- sm
- sn
- so
- sr
- srn
- ss
- st
- stq
- su
- sv
- sw
- szl
- ta
- te
- tet
- tg
- th
- ti
- tk
- tl
- tlh
- tn
- to
- tpi
- tr
- ts
- tt
- tum
- tw
- ty
- udm
- ug
- uk
- ur
- uz
- ve
- vec
- vi
- vls
- vo
- wa
- war
- wo
- wuu
- xal
- xh
- yi
- yo
- za
- zea
- zh
- zh_classical
- zh_min_nan
- zh_yue
- zu
Static Wikipedia February 2008 (no images)
aa - ab - af - ak - als - am - an - ang - ar - arc - as - ast - av - ay - az - ba - bar - bat_smg - bcl - be - be_x_old - bg - bh - bi - bm - bn - bo - bpy - br - bs - bug - bxr - ca - cbk_zam - cdo - ce - ceb - ch - cho - chr - chy - co - cr - crh - cs - csb - cu - cv - cy - da - de - diq - dsb - dv - dz - ee - el - eml - en - eo - es - et - eu - ext - fa - ff - fi - fiu_vro - fj - fo - fr - frp - fur - fy - ga - gan - gd - gl - glk - gn - got - gu - gv - ha - hak - haw - he - hi - hif - ho - hr - hsb - ht - hu - hy - hz - ia - id - ie - ig - ii - ik - ilo - io - is - it - iu - ja - jbo - jv - ka - kaa - kab - kg - ki - kj - kk - kl - km - kn - ko - kr - ks - ksh - ku - kv - kw - ky - la - lad - lb - lbe - lg - li - lij - lmo - ln - lo - lt - lv - map_bms - mdf - mg - mh - mi - mk - ml - mn - mo - mr - mt - mus - my - myv - mzn - na - nah - nap - nds - nds_nl - ne - new - ng - nl - nn - no - nov - nrm - nv - ny - oc - om - or - os - pa - pag - pam - pap - pdc - pi - pih - pl - pms - ps - pt - qu - quality - rm - rmy - rn - ro - roa_rup - roa_tara - ru - rw - sa - sah - sc - scn - sco - sd - se - sg - sh - si - simple - sk - sl - sm - sn - so - sr - srn - ss - st - stq - su - sv - sw - szl - ta - te - tet - tg - th - ti - tk - tl - tlh - tn - to - tpi - tr - ts - tt - tum - tw - ty - udm - ug - uk - ur - uz - ve - vec - vi - vls - vo - wa - war - wo - wuu - xal - xh - yi - yo - za - zea - zh - zh_classical - zh_min_nan - zh_yue - zu