Economy of the United Kingdom
Background to the schools Wikipedia
The articles in this Schools selection have been arranged by curriculum topic thanks to SOS Children volunteers. Sponsor a child to make a real difference.
| Economy of the United Kingdom | |
|---|---|
 Canary Wharf business district in London |
|
| Rank | 7th (nominal) / 8th (PPP) (3rd and 2nd in Europe respectively) |
| Currency | Pound sterling (GBP) |
| Fiscal year | 6 April – 5 April |
| Trade organisations | EU, BCN, OECD and WTO |
| Statistics | |
| GDP |
$2.480 trillion (2011) (nominal; 7th) $2.253 trillion (2011) (PPP; 8th) |
| GDP growth | -0.1% (2012 est.) ( ONS) |
| GDP per capita | $39,600 (2011) (nom; 20th) $36,000 (2011) (PPP; 17th) |
| GDP by sector | agriculture: 0.7%, industry: 21.5%, services: 77.8% (2011 est.) |
| Inflation ( CPI) | CPI:2.7%, RPI 2.9% (November 2012) |
| Population below poverty line |
14% with household income below 60% of UK median income (2006 est.) |
| Gini coefficient | 0.36 (2008) |
| Labour force | 31.72 million (2011 est.) |
| Labour force by occupation |
agriculture: 1.4%, industry: 18.2%, services: 80.4% (2006 est.) |
| Unemployment | 7.7% (2.49 million) (3 months to November 2012; down 37,000 on 3 months to October 2012, down 0.1 percentage point.) |
| Average gross salary | €4,108 / $5,546, monthly (2006) |
| Average net salary | €2,749 / $3,712, monthly (2006) |
| Main industries |
List
|
| Ease of Doing Business Rank | 7th |
| External | |
| Exports | $479.2 billion (2011 est.) |
| Export goods | Manufactured goods, sup, chemicals; food, beverages, tobacco |
| Main export partners | Germany 11.6%, US 10.6%, Netherlands 8.4%, France 7.8%, Republic of Ireland 6.4%, Belgium 5.7% (2011) |
| Imports | $639 billion (2011 est.) |
| Import goods | Manufactured goods, machinery, fuels; foodstuffs |
| Main import partners | Germany 13.2%, China 8.7%, Netherlands 7.5%, US 6.1%, France 6%, Norway 5%, Belgium 5% (2011) |
| FDI stock | $1.169 trillion (31 December 2010 est.) |
| Gross external debt | $9.836 trillion (30 June 2011) ( 2nd) |
| Public finances | |
| Public debt | £977 billion 88.7% of GDP (2012 est.) |
| Budget deficit | £155 billion (2009–10 FY) £120 billion (2011-12 FY). Budget deficit proposed for 2012-2013 is £90 billion (6% of GDP) |
| Revenues | £592 billion (2012-2013 FY) |
| Expenses | £682 billion (2012-2013 FY) |
| Economic aid | $10 billion (2012) (donor) |
| Credit rating | Standard & Poor's: AA1 (Domestic) AA1 (Foreign) AA1 (T&C Assessment) Outlook: Negative Moody's: AA1 Outlook: Negative Watch Fitch: AAA Outlook: NEGATIVE |
| Foreign reserves | $127.8 billion (Aug 2012) |
|
Main data source: CIA World Fact Book |
|
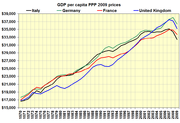
The economy of the United Kingdom is the sixth-largest national economy in the world measured by nominal GDP and eighth-largest measured by purchasing power parity (PPP), and the third-largest in Europe measured by nominal GDP (after Germany and France) and second-largest measured by PPP (after Germany). The UK's GDP per capita is the 22nd highest in the world in nominal terms and the 22nd highest measured by PPP. The British economy encompasses (in descending order of size) the economies of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
In the 18th century, as the transcendental agent of the Renaissance with the basis of unsurpassed national wealth and trade power, the UK was the first country in the world to industrialise for its industrial development and during the 19th century possessed a dominant role in the global economy. From the late-19th century the Second Industrial Revolution in the United States and Germany presented an increasing economic challenge to Britain. Despite victory, the costs of fighting both the First World War and Second World War further weakened the accountability of UK's public finance and resulted in the collapse of the British Empire, and by 1945 it had been superseded by the United States as the world's dominant economic power. However, it still maintains a significant role, such as the area of financial industry in the world economy, and the UK plans on the knowledge economy right underway.
The UK has one of the world's most globalised economies. London is the world's largest financial centre alongside New York and has the largest city GDP in Europe. As of December 2010 the UK had the third-largest stock of both inward and outward foreign direct investment (in each case after the United States and France). The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest national aerospace industry, depending upon the method of measurement. The pharmaceutical industry plays an important role in the UK economy and the country has the third-highest share of global pharmaceutical R&D expenditures (after the United States and Japan). The British economy is boosted by North Sea oil and gas reserves, valued at an estimated £250 billion in 2007.
Since 1979 and the latter Margaret Thatcher Government, most state-owned companies were privatised and opened to public competition and listed in the UK's financial market to augment demand as well as supply in the British economy, and UK government introduced indirect taxes rather than direct taxes to the public. Government involvement in the British economy is exercised by HM Treasury, headed by the Chancellor of the Exchequer. The Bank of England is the UK's central bank and its Monetary Policy Committee is responsible for setting interest rates. The currency of the UK is the pound sterling, which is also the world's third-largest reserve currency after the U.S. dollar and the euro. The UK is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the European Union, the G7, the G8, the G20, the International Monetary Fund, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, the World Bank, the World Trade Organisation and the United Nations. The UK is currently ranked seventh in the world in the World Bank's Ease of Doing Business Index.
The UK economy has been weak in recent years following the late 2000s recession with growth largely flat since 2010. The UK experienced a double dip recession which was the longest and deepest in 50 years between Q4 2011 and Q2 2012; however recent figures have shown the UK economy improving, unemployment fell to 7.7% in the 3 months to November, this is the lowest for 18 months, and the UK economy started to grow again in Q3 2012, growing by 1.0% - the fastest rate of GDP growth since Q3 2007. There are warnings from some economists and the Bank of England that the UK economy might slip back in to recession in the Q4 of 2012; however latest unemployment statistics from the ONS show unemployment falling at its fastest rate since 2001 and a leading index complied by the OECD shows momentum continuing to build in the British economy with growth 'firming up'. However, in February 2013, the UK lost its top AAA credit rating for first time since 1978.
History
1945 to 1979
Following the end of the Second World War, the United Kingdom enjoyed a long period without a major recession (from 1945 to 1973) and a rapid growth in prosperity in the 1950s and 1960s. According to the OECD, the annual rate of growth (percentage change) between 1960 and 1973 averaged 2.9%, although this figure was far behind the rates of other European countries such as France, West Germany and Italy.
However, following the severe shock of the 1973 oil crisis and the 1973–1974 stock market crash, the British economy had fallen into recession by the time Edward Heath's Conservative Party government had been ousted by the Labour Party as Harold Wilson moved into office for the second time, forming a minority government on 4 March after the general election on 28 February ended in a hung parliament, and then securing a three-seat majority in a second election in October that year.
GDP had fallen by 1.1%, recording weaker growth than other European nations in the 1970s overall; even when the recession ended in 1975, the economy was still blighted by double-digit inflation and unemployment was rising. Overall economic picture deteriorated with accelerating inflation and slumping pound sterling pushing the UK to accept an IMF rescue to the tune of £2.3bn loan. The IMF forced Chancellor Denis Healey into harsh public spending cuts and austere economic measures as part of reforms put through to improve the economic situation and as a condition to the rescue package. Soon enough, in 1979 the government fell.
1979 to 1997
A new period of neo-liberal economics began in 1979 with the election of Margaret Thatcher who won the general election on 3 May that year to return the Conservative Party to government after five years of Labour rule.
During the 1980s most state-owned enterprises were privatised, taxes cut and markets deregulated. GDP fell 5.9% at first but growth rose to 5% at its peak in 1988, one of the highest rates of any European nation.
However, Thatcher's modernisation of the British economy was far from trouble free; her battle against inflation resulted in mass unemployment with the jobless count passing 3,000,000 by the start of 1982 compared to 1,500,000 three years previously. This was in part due to the closure of outdated factories and coalpits which were no longer economically viable; this process continued for most of the rest of the decade. Unemployment peaked at nearly 3,300,000 during 1984 before falling dramatically in the final three years of the decade, standing at just over 1,600,000 by the end of 1989. However, the British economy slid into another recession during the second half of 1990, concurrent with a global recession, and caused the economy to shrink by a total of 8% from peak to trough and unemployment to increase from around 1,600,000 to nearly 3,000,000 by early 1993, when the recession ended, and the subsequent economic recovery was extremely strong. Unlike the early 1980s recession the recovery saw a rapid and substantial fall in unemployment, which was down to 1,700,000 by 1997.
1997 to 2008
The Labour Party, led by Tony Blair, returned to power in May 1997 after 18 years in opposition. During Blair's 10 years in office there were 40 successive quarters of economic growth, lasting until the second quarter of 2008. The previous 15 years had seen one of the highest economic growth rates of major developed economies during that time and certainly the strongest of any European nation. GDP growth had briefly reached 4% in the early 1990s, gently declining thereafter. Peak growth was relatively anaemic compared to prior decades, such as the 6.5% peak in the early 1970s, although growth was smoother and more consistent. Annual growth rates averaged 2.68% between 1992–2007 according to the IMF, with the finance sector growth contributing a greater part than previously. This extended period of growth ended in 2008 when the United Kingdom suddenly entered a recession – its first for nearly two decades – brought about by the global financial crisis. Beginning with the collapse of Northern Rock, which was taken into public ownership in February 2008, other banks had to be partly nationalised. The Royal Bank of Scotland Group, which at its peak was the fifth-largest in the world by market capitalisation, was effectively nationalised on 13 October 2008. By mid 2009, HM Treasury had a 70.33% controlling shareholding in RBS, and a 43% shareholding through UK Financial Investments Limited of Lloyds Banking Group. The recession saw unemployment rise from just over 1,600,000 in January 2008 to nearly 2,500,000 in October 2009.
The UK economy had been one of the strongest EU economies in terms of inflation, interest rates and unemployment, all of which remained relatively low until the 2008–09 recession. Unemployment has since reached a peak of just under 2.5 million (7.8%), the highest level since early 1990s, although still far lower than some other European nations. However, interest rates have been reduced to 0.5%. During August 2008 the IMF warned that the UK economic outlook had worsened due to a twin shock: financial turmoil as well as rising commodity prices. Both developments harm the UK more than most developed countries, as the UK obtains revenue from exporting financial services while recording deficits in finished goods and commodities, including food. In 2007, the UK had the world's third largest current account deficit, due mainly to a large deficit in manufactured goods. During May 2008, the IMF advised the UK government to broaden the scope of fiscal policy to promote external balance. Although the UK's "labour productivity per person employed" has been progressing well over the last two decades and has overtaken productivity in Germany, it still lags around 20% behind France's level, where workers have a 35-hour working week. The UK's "labour productivity per hour worked" is currently on a par with the average for the "old" EU (15 countries). In 2010, the United Kingdom ranked 26th on the Human Development Index.
2008 to present
The UK entered a recession in Q2 of 2008, according to the UK Office for National Statistics (ONS) and exited it in Q4 of 2009. The revised ONS figures of November 2009 showed that the UK had suffered six consecutive quarters of negative growth. As of the end of November 2009, the economy had shrunk by 4.9%, making the 2008–2009 recession the longest since records began. In December 2009, the Office for National Statistics revised figures for the third quarter of 2009 showed that the economy shrank by 0.2%, compared to a 0.6% fall the previous quarter.
In Q1 of 2012, the UK economy entered a double-dip recession, in the process posting three consecutive negative quarters of growth. While the first half of 2012 saw inflationary pressures subside and business confidence increase, a number of fundamental weaknesses remained, most notably a decline in the productivity of British business. As of the end of Q2 of 2012, the UK economy had contracted 1.2% in three quarters. The 'Jubilee' effect has been blamed for the contraction in Q2 2012 due to lost working days. Figures from July and August indicate strong growth returning. Services showed increased expansion while manufacturing posted growth of 3.2% in July, the strongest since July 2002. Industrial production increased 2.9%, the strongest since February 1987. In Q3 2012 the UK's economy bounced back from recession very strongly with 1% growth, then fastest since Autumn 2007.
Macroeconomic trend
Below is a table of the trend of gross domestic product of United Kingdom at market prices estimated by the International Monetary Fund, with figures in millions of pounds sterling.
| Year | Gross domestic product | US dollar exchange | Inflation index (2000=100) |
Per Capita Income (as % of USA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1925 | 4,466 | £0.21 | 3 | 61.79 |
| 1930 | 4,572 | £0.21 | 3 | 66.08 |
| 1935 | 4,676 | £0.20 | 2 | 85.67 |
| 1940 | 7,117 | £0.26 | 3 | 74.28 |
| 1945 | 9,816 | £0.25 | 4 | 50.93 |
| 1950 | 13,162 | £0.36 | 5 | 38.26 |
| 1955 | 19,264 | £0.36 | 6 | 42.54 |
| 1960 | 25,678 | £0.36 | 7 | 47.86 |
| 1965 | 35,781 | £0.36 | 9 | 49.96 |
| 1970 | 51,515 | £0.42 | 11 | 44.04 |
| 1975 | 105,773 | £0.45 | 20 | 55.54 |
| 1980 | 230,695 | £0.42 | 43 | 78.57 |
| 1985 | 354,952 | £0.77 | 60 | 46.84 |
| 1990 | 557,300 | £0.56 | 76 | 76.62 |
| 1995 | 718,383 | £0.63 | 92 | 71.84 |
| 2000 | 953,576 | £0.65 | 100 | 72.29 |
| 2005 | 1,209,334 | £0.54 | 107 | 90.17 |
For purchasing power parity comparisons, the US Dollar is exchanged at £0.66
Below is a table of the trend of CPI of United Kingdom:
| Wikinews has related news: UK enters recession |
| Year | CPI |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 3,70 |
| 2009 | 2,90 |
| 2008 | 3,10 |
| 2007 | 2,10 |
| 2006 | 3,00 |
Sectors
Agriculture, hunting, forestry, and fishing

Agriculture is intensive, highly mechanised, and efficient by European standards, producing about 60% of food needs, with less than 1.6% of the labour force (535,000 workers). It contributes around 0.6% of British national value added. Around two-thirds of the production is devoted to livestock, one-third to arable crops. Agriculture is subsidised by the European Union's Common Agricultural Policy.
The UK retains a significant, though reduced, fishing industry. Its fleets, based in towns such as Kingston upon Hull, Grimsby, Fleetwood, Newlyn, Great Yarmouth, Peterhead, Fraserburgh, and Lowestoft, bring home fish ranging from sole to herring.
The Blue Book 2006 (page 110) reports that "agriculture, hunting, forestry and fishing" added gross value of £10,323 million (at 2006 prices) to the UK economy in 2004.
The UK is also rich in a number of natural resources including coal, petroleum, natural gas, tin, limestone, iron ore, salt, clay, chalk, gypsum, lead, silica and an abundance of arable land.
Construction
The Blue Book 2006 reports that this industry added gross value of £64,747 million to the UK economy in 2004. It is the fastest growing sector of the economy – after the 2010 Recession.
Production industries
Electricity, gas and water supply
The Blue Book 2006 reports that this sector added gross value of £17,103 million to the UK economy in 2004. The United Kingdom is expected to launch the building of new nuclear reactors to replace existing generators and to boost UK's energy reserves.
Manufacturing

In 2009 the UK manufacturing sector generated approximately £140 billion in gross value added and employed around 2.6 million people. Of the approximately £16 billion invested in R&D by UK businesses in 2008, approximately £12 billion was by manufacturing businesses. In 2008, the UK was the sixth-largest manufacturer in the world measured by value of output.
In 2008 around 180,000 people in the UK were directly employed in the UK automotive manufacturing sector. In that year the sector had a turnover of £52.5 billion, generated £26.6 billion of exports and produced around 1.45 million passenger vehicles and 203,000 commercial vehicles. The UK is a major centre for engine manufacturing, and in 2008 around 3.16 million engines were produced in the country.
The aerospace industry of the UK is the second- or third-largest aerospace industry in the world, depending upon the method of measurement. The industry employs around 113,000 people directly and around 276,000 indirectly and has an annual turnover of around £20 billion. British companies with a major presence in the industry include BAE Systems (the world's second-largest defence contractor) and Rolls-Royce (the world's second-largest aircraft engine maker). Foreign aerospace companies active in the UK include EADS and its Airbus subsidiary, which employs over 13,000 people in the UK.
The pharmaceutical industry employs around 67,000 people in the UK and in 2007 contributed £8.4 billion to the UK's GDP and invested a total of £3.9 billion in research and development. In 2007 exports of pharmaceutical products from the UK totalled £14.6 billion, creating a trade surplus in pharmaceutical products of £4.3 billion. The UK is home to GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca, respectively the world's third- and seventh-largest pharmaceutical companies.
Mining and quarrying
The Blue Book 2006 reports that this sector added gross value of £21,876 million to the UK economy in 2004. In 2007 the UK had a total energy output of 9.5 quadrillion Btus, of which the composition was oil (38%), natural gas (36%), coal (13%), nuclear (11%) and other renewables (2%). In 2009, the UK produced 1.5 million barrels per day (bbl/d) of oil and consumed 1.7 million bbl/d. Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of oil since 2005. As of 2010 the UK has around 3.1 billion barrels of proven crude oil reserves, the largest of any EU member state.
In 2009 the UK was the 13th largest producer of natural gas in the world and the largest producer in the EU. Production is now in decline and the UK has been a net importer of natural gas since 2004. In 2009 the UK produced 19.7 million tons of coal and consumed 60.2 million tons. In 2005 it had proven recoverable coal reserves of 171 million tons. It has been estimated that identified onshore areas have the potential to produce between 7 billion tonnes and 16 billion tonnes of coal through underground coal gasification (UCG). Based on current UK coal consumption, these volumes represent reserves that could last the UK between 200 and 400 years.
The UK is home to a number of large energy companies, including two of the six oil and gas " supermajors" – BP and Royal Dutch Shell – and BG Group.
Service industries
The service sector is the dominant sector of the UK economy, and contributes around 73% of GDP.
Creative industries
The creative industries accounted for 7% GVA in 2005 and grew at an average of 6% per annum between 1997 and 2005. Key areas include London and the North West of England which are the two largest creative industry clusters in Europe.
Education, health and social work
In 2008 the education, health and social work sector had a total gross value added of around £170 billion, of which around £145 billion was compensation to employees. In 2008 the sector had a total gross capital formation of around £17.7 billion.
In 2008 health and social work had a gross value added of around £93.7 billion. In the UK the majority of the healthcare sector consists of the state funded and operated National Health Service (NHS), which accounts for over 80% of all healthcare spending in the UK and has a workforce of around 1.7 million, making it the largest employer in Europe, and putting it amongst the largest employers in the world. The NHS operates independently in each of the four constituent countries of the UK. The NHS in England is by far the largest of the four parts and had a turnover of £92.5 billion in 2008.
In 2008 education had a gross value added of around £76 billion. In 2007/08 higher education institutions in the UK had a total income of £23 billion and employed a total of 169,995 staff. In 2007/08 there were 2,306,000 higher education students in the UK (1,922,180 in England, 210,180 in Scotland, 125,540 in Wales and 48,200 in Northern Ireland).
Financial and business services
This industry added gross value of £86,145 million to the UK economy in 2004. The UK's exports of financial and business services make a significant positive contribution towards the country's balance of payments.
London is a major centre for international business and commerce and is one of the three "command centres" of the global economy (alongside New York City and Tokyo). There are over 500 banks with offices in London, and it is the leading international centre for banking, insurance, Eurobonds, foreign exchange trading and energy futures. London's financial services industry is primarily based in the City of London and Canary Wharf. The City houses the London Stock Exchange, the London International Financial Futures and Options Exchange, the London Metal Exchange, Lloyds of London, and the Bank of England. Canary Wharf began development in the 1980s and is now home to major financial institutions such as Barclays Bank, Citigroup and HSBC, as well as the UK Financial Services Authority.) London is also a major centre for other business and professional services, and four of the six largest law firms in the world are headquartered there.
Several other major UK cities have large financial sectors and related services. Edinburgh has one of the large financial centres in Europe and is home to the headquarters of the Royal Bank of Scotland Group and Standard Life. Leeds is now the UK's largest centre for business and financial services outside London, and the largest centre for legal services in the UK after London.
Hotels and restaurants
The Blue Book 2006 reports that this industry added gross value of £33,074 million to the UK economy in 2004.
Other social and personal services
This sector includes value added by private households with employees and extraterritorial organisations. The Blue Book 2006 reports that this sector added gross value of £55,543 million to the UK economy in 2004.
Public administration and defence
The Blue Book 2006 reports that this sector added gross value of £55,280 million to the UK economy in 2004.
Real estate and renting activities

The real estate and renting activities sector includes the letting of dwellings and other related business support activities. The Blue Book 2006 reports that the lettings industry added gross value of £83,037 million to the UK economy in 2004 while other real estate and business support activities added gross value of £175,333 million. Notable real estate companies in the United Kingdom include British Land and The Peel Group.
The UK property market boomed for the seven years up to 2008 and in some areas property trebled in value over that period. The increase in property prices had a number of causes: low interest rates, credit growth, economic growth, rapid growth in buy to-let property investment, foreign property investment in London and planning restrictions on the supply of new housing.
Tourism
Tourism is very important to the British economy. With over 27 million tourists arriving in 2004, the United Kingdom is ranked as the sixth major tourist destination in the world. London, by a considerable margin, is the most visited city in the world with 15.6 million visitors in 2006, ahead of 2nd placed Bangkok (10.4 million visitors) and 3rd placed Paris (9.7 million).
Transport, storage and communication

The Blue Book 2006 reports that the transport and storage industry added gross value of £49,516 million to the UK economy in 2004 while the communication industry added a gross value of £29,762 million.
The UK has a radial road network of 46,904 kilometres (29,145 mi) of main roads, with a motorway network of 3,497 kilometres (2,173 mi). There are a further 213,750 kilometres (132,818 mi) of paved roads. There is a railway infrastructure company Network Rail, with train operating companies including foreign state owned companies including Deutsche Bahn AG of 16,116 km (10,014 mi) in Great Britain and 303 route km (189 route mi) in Northern Ireland run by Northern Ireland Railways, which carries over 18,000 passenger trains and 1,000 freight trains per day. Urban rail networks are well developed in Glasgow, Liverpool and London as well as other cities. Plans are now being considered to build new high speed lines linking all major cities by 2025.
The Highways Agency is the executive agency responsible for trunk roads and motorways in England apart from the privately owned and operated M6 Toll. The Department for Transport states that traffic congestion is one of the most serious transport problems and that it could cost England an extra £22 billion in wasted time by 2025 if left unchecked. According to the government-sponsored Eddington report of 2006, congestion is in danger of harming the economy, unless tackled by road pricing and expansion of the transport network.
In the year from October 2009 to September 2010 UK airports handled a total of 211.4 million passengers. In that period the three largest airports were London Heathrow Airport (65.6 million passengers), Gatwick Airport (31.5 million passengers) and London Stansted Airport (18.9 million passengers). London Heathrow Airport, located 24 kilometres (15 mi) west of the capital, has the most international passenger traffic of any airport in the world. and is the hub for the UK flag carrier British Airways, as well as BMI and Virgin Atlantic. London's six commercial airports form the world's largest city airport system measured by passenger traffic.
Wholesale and retail trade

This sector includes the motor trade, auto repairs, personal and household goods industries. The Blue Book 2006 reports that this sector added gross value of £127,520 million to the UK economy in 2004.
The UK grocery market is dominated by five companies – Asda (owned by Wal-Mart Stores), The Co-operative Food, Morrisons, Sainsbury's and Tesco – which together have a market share of over 80%.
London is a major retail centre and in 2010 had the highest non-food retail sales of any city in the world, with a total spend of around £64.2 billion. The UK-based Tesco is the third-largest retailer in the world measured by revenues (after Wal-Mart Stores and Carrefour) and is the current leader in the UK market with around a 30% share.
Currency
London is the world capital for foreign exchange trading. The highest daily volume, counted in trillions of dollars US, is reached when New York enters the trade. The currency of the UK is the pound sterling, represented by the symbol £. The Bank of England is the central bank, responsible for issuing currency. Banks in Scotland and Northern Ireland retain the right to issue their own notes, subject to retaining enough Bank of England notes in reserve to cover the issue. Pound sterling is also used as a reserve currency by other governments and institutions, and is the third-largest after the U.S. dollar and the euro.
The UK chose not to join the euro at the currency's launch. The government of former Prime Minister Tony Blair had pledged to hold a public referendum for deciding membership should " five economic tests" be met. Until relatively recently there was debate over whether or not the UK should abolish its currency Pound Sterling and join the Euro. In 2007 the British Prime Minister, Gordon Brown, pledged at the time to hold a public referendum based on certain tests he set as Chancellor of the Exchequer. When assessing the tests, Gordon Brown concluded that while the decision was close, the United Kingdom should not yet join the Euro. He ruled out membership for the foreseeable future, saying that the decision not to join had been right for Britain and for Europe. In particular, he cited fluctuations in house prices as a barrier to immediate entry. Public opinion polls have shown that a majority of Britons have been opposed to joining the single currency for some considerable time and this position has now hardened further. In 2005, more than half (55%) of the UK were against adopting the currency, while 30% were in favour. The current government, a Conservative and Liberal Democrat coalition, is opposed to membership.
Exchange rates
(average for of each year), in USD (US dollar) and EUR (euro) per GBP; and inversely: GBP per USD and EUR. ( Synthetic Euro XEU before 1999). Caution: these averages conceal wide intra-year spreads. The coefficient of variation gives an indication of this. It also shows the extent to which the pound tracks the euro or the dollar. Note the effect of Black Wednesday in late 1992 by comparing the averages for 1992 with the averages for 1993.
| Year | £/USD | USD/£ | C.Var | £/XEU | XEU/£ | C.Var | |
| 1990 | £0.5633 | $1.775 | £0.7161 | ₠1.397 | |||
| 1991 | £0.5675 | $1.762 | £0.7022 | ₠1.424 | |||
| 1992 | £0.5699 | $1.755 | £0.7365 | ₠1.358 | |||
| 1993 | £0.6663 | $1.501 | £0.7795 | ₠1.283 | |||
| 1994 | £0.6536 | $1.53 | £0.7742 | ₠1.292 | |||
| 1995 | £0.6338 | $1.578 | £0.82 | ₠1.22 | |||
| 1996 | £0.6411 | $1.56 | £0.8029 | ₠1.245 | |||
| 1997 | £0.6106 | $1.638 | £0.6909 | ₠1.447 | |||
| 1998 | £0.6037 | $1.656 | £0.6779 | ₠1.475 |
| Year | £/USD | USD/£ | C.Var | £/EUR | EUR/£ | C.Var | |
| 1999 | £0.6185 | $1.617 | £0.6595 | €1.516 | |||
| 2000 | £0.6609 | $1.513 | £0.6099 | €1.64 | |||
| 2001 | £0.6943 | $1.44 | £0.6223 | €1.607 | |||
| 2002 | £0.6664 | $1.501 | £0.6289 | €1.59 | |||
| 2003 | £0.6123 | $1.633 | £0.6924 | €1.444 | |||
| 2004 | £0.5461 | $1.832 | 2.26% | £0.6787 | €1.474 | 1.92% | |
| 2005 | £0.55 | $1.82 | 3.47% | £0.6842 | €1.462 | 1.27% | |
| 2006 | £0.5435 | $1.842 | 3.79% | £0.6821 | €1.466 | 1.11% | |
| 2007 | £0.4999 | $2.001 | 1.97% | £0.6848 | €1.461 | 2.4% | |
| 2008 | £0.5499 | $1.835 | £0.7964 | €1.226 | |||
| 2009 | £0.641 | $1.566 | £0.8914 | €1.123 | |||
| 2010 | £0.6474 | $1.546 | £0.8586 | €1.166 |
1 GBP in USD since 1971
- Source: OANDA.COM Historical Currency Converter
- For consistency and comparison purposes, coefficient of variation is measured on both the "per pound" ratios, although it is conventional to show the forex rates as dollars per pound and pounds per euro.
Regional variations

The strength of the UK economy varies from country to country and from region to region. Excluding the effects of North Sea Oil and Gas (officially included in the Extra-regio), England has the highest Gross value added (GVA) with Scotland close behind, though Scotland has a higher figure, estimated as approximately £24 000 per capita in 2009, once a geographical share of oil and gas is assigned. Scotland had the best rate of per capita growth over the preceding 12 months, declining by 1.4%, ahead of the best performing region of England which was the North West with a decline of 1.9%. GVA per capita figures for 2009 for the four countries of the United Kingdom (excluding oil and gas) are:
| Rank | Place | GVA per capita in pounds (dollars in parenthesis) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | England | 20 442 ($31,545) |
| 2 | Scotland | 19 744 ($30,468) |
| 3 | Northern Ireland | 15 795 ($24,374) |
| 4 | Wales | 14 842 ($22,903) |
Within England, GVA per capita is highest in London. The following table shows the GVA (2009) per capita of the 9 statistical regions of England ( NUTS).
| Rank | Place | GVA per capita in pounds |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Greater London | 34,200 ($52,776) |
| 2 | South East England | 20,923 ($32,287) |
| 3 | East of England | 18,591 ($28,689) |
| 4 | South West England | 18,211 ($28,102) |
| 5 | East Midlands | 17,349 ($26,772) |
| 6 | North West England | 17,263 ($26,639) |
| 7 | West Midlands | 16,788 ($25,906) |
| 8 | Yorkshire and the Humber, England | 16,569 ($25,568) |
| 9 | North East England | 15,621 ($24,106) |
Two of the richest 10 areas in the European Union are in the United Kingdom. Inner London is number 1 with a GDP per capita of €65 138, and Berkshire, Buckinghamshire and Oxfordshire is number 7 with a GDP per capita of €37 379. Edinburgh is also one of the largest financial centres in Europe.
At the other end of the scale, Cornwall has the lowest GVA per head of any county or unitary authority in England, and it has received EU Convergence funding (formerly Objective One funding) since 2000.
Government involvement
Government involvement throughout the economy is exercised by the Chancellor of the Exchequer who heads HM Treasury. In recent years, the UK economy has been managed in accordance with principles of market liberalisation and low taxation and regulation. Since 1997, the Bank of England's Monetary Policy Committee, headed by the Governor of the Bank of England, has been responsible for setting interest rates at the level necessary to achieve the overall inflation target for the economy that is set by the Chancellor each year. The Scottish Government, subject to the approval of the Scottish Parliament, has the power to vary the basic rate of income tax payable in Scotland by plus or minus 3 pence in the pound, though this power has not yet been exercised.
In the 20 year period from 1986/87 to 2006/07 government spending in the UK averaged around 40% of GDP. As a result of the 2007–2010 financial crisis and the late-2000s global recession government spending increased to a historically high level of 48% of GDP in 2009–10, partly as a result of the cost of a series of bank bailouts. In July 2007, the UK had government debt at 35.5% of GDP. This figure rose to 56.8% of GDP by July 2009. As of June 2010 there were approximately 6,051,000 public sector employees in the UK (compared to approximately 23,107,000 private sector employees).
Taxation and borrowing
Taxation in the United Kingdom may involve payments to at least two different levels of government: local government and central government ( HM Revenue & Customs). Local government is financed by grants from central government funds, business rates, council tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those from on-street parking. Central government revenues are mainly income tax, national insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty.
These data show the tax burden (personal and corporate) and national debt as a percentage of GDP. Samples are taken at 10 year intervals (snapshots, but the rolling averages are very close).
| Year | Tax | Debt |
|---|---|---|
| 1975/6 | 54% | 43% |
| 1985/6 | 44% | 43% |
| 1995/6 | 43% | 38% |
| 2005/6* | 46% | 40% |
| 2009/10 | 57% | 68% |
- (Source: HM Treasury Public Finances Databank)
- (* — Projected)
Economic indices
The money Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for the United Kingdom, at market prices, in 2009 was £1 396 billion (or $2 003 billion) according to the Office for National Statistics in February 2010.
| Year | GDP (billions of GBP) | GDP Change |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 3.9% | |
| 2001 | 2.5% | |
| 2002 | 2.1% | |
| 2003 | 2.8% | |
| 2004 | 3.0% | |
| 2005 | 2.2% | |
| 2006 | 2.9% | |
| 2007 | 2.6% | |
| 2008 | 1 448 | 0.6% |
| 2009 | 1 396 | −4.9% |
| 2010 | 2.1% | |
| 2011 | 0.6% |
| Income distribution lowest 10% highest 10% |
(2010) 1% 31% |
| Consumer prices inflation | RPI: 3.5% (April 2012), CPI: 3.0% (April 2012) |
| Labour force composition services government manufacturing/construction energy agriculture |
(2004) 46% 28% 24% 1% 1% |
| Industrial growth | −0.3% (1999) |
| Electricity production | 368.6 TWh (2007 est.) |
| Electricity production composition fossil fuel hydro nuclear renewables imports |
(2004) 74.13% 1.1% 19.26% 3.55% 1.96% |
| Electricity consumption | 345.8 TWh (2007 est.) |
| Electricity exports | 1.272 TWh (2008 est.) |
| Electricity imports | 12.29 TWh (2008 est.) |
| Agriculture products | cereals, oilseed, potatoes, vegetables; cattle, sheep, poultry; fish |
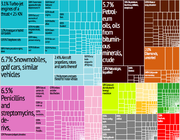
| Exported commodities | manufactured goods, fuels, chemicals; food, beverages (notably Scotch whisky), tobacco |
| Imported commodities | manufactured goods, machinery, fuels; foodstuffs |
Exports
In 2007 UK exports were valued at £221bn.
- Food and drink exports were valued at £9.7bn (2005)
- UK total arms exports were valued at £7.1bn (2005)
UK export figures are boosted 10% by high levels of Missing trader fraud according to the Office for National Statistics.
Poverty
The United Kingdom is a developed country with social welfare infrastructure, thus discussions surrounding poverty tend to be of relative poverty rather than absolute poverty. According to the OECD, the UK is in the lower half of developed country rankings for poverty rates, doing better than Germany, Italy and the US and less well than France, Austria, Hungary, Slovakia and the Scandinavian countries.
The poverty line in the UK is commonly defined as being 60% of the median household income. In 2007–2008, this was calculated to be £115 per week for single adults with no dependent children; £199 per week for couples with no dependent children; £195 per week for single adults with two dependent children under 14; and £279 per week for couples with two dependent children under 14. In 2007–2008, 13.5 million people, or 22% of the population, lived below this line. This is a higher level of relative poverty than all but four other EU members. In the same year, 4.0 million children, 31% of the total, lived in households below the poverty line, after housing costs were taken into account. This is a decrease of 400,000 children since 1998–1999.