
List of countries by system of government
Did you know...
This Schools selection was originally chosen by SOS Children for schools in the developing world without internet access. It is available as a intranet download. A good way to help other children is by sponsoring a child
This is a list of countries categorized by system of government.
Alphabetical list of countries
| Name | Constitutional basis | Head of state | Basis of executive legitimacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| n/a | n/a | No constitutionally-defined basis to current regime | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| n/a | n/a | No constitutionally-defined basis to current regime | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency and ministry are subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency independent of legislature; ministry subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Executive | Monarch personally exercises power in concert with other institutions | |
| Constitutional monarchy | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Ceremonial | Ministry is subject to parliamentary confidence | |
| Absolute monarchy | Executive | All authority vested in absolute monarch | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Power constitutionally linked to a single political movement | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature | |
| Republic | Executive | Presidency is independent of legislature |
Notes on colour-code
- orange - parliamentary republics
- green - presidential republics, executive presidency linked to a parliament
- yellow - presidential republics, semi-presidential system
- blue - presidential republics, full presidential system
- red - parliamentary constitutional monarchies in which the monarch does not personally exercise power
- magenta - constitutional monarchies in which the monarch personally exercises power, often (but not always) alongside a weak parliament
- purple - absolute monarchies
- brown - republics where the dominant role of a single party is codified in the constitution
- beige - states where constitutional provisions for government have been suspended
- grey - countries which do not fit any of the above systems
Note that several states constitutionally deemed to be multiparty republics are broadly described by outsiders as authoritarian states. This chart aims to represent de jure form of government, not de facto degree of democracy. Those more interested in a version reflecting such judgements may be interested in seeing this map from Freedom House. 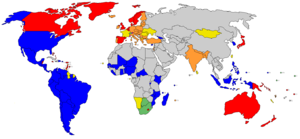 .
.
Systems of Governance
Presidential / Separated republics
These are systems in which a president is the active head of the executive branch of government and is elected and remains in office independently of the legislature. The following list includes democratic and non-democratic states:
Full presidential systems
In full presidential systems, the president is both head of state and head of government. There is generally no prime minister, although if one exists he or she serves purely at the pleasure of the president.
Semi-presidential systems
In semi-presidential systems, there is usually both a president and a prime minister. In such systems, the President has genuine executive authority, unlike in a parliamentary republic, but some of the role of a head of government is exercised by the prime minister, who is also leader of the legislature.
|
Parliamentary republics
A parliamentary republic is a system in which a prime minister is the active head of the executive branch of government and also leader of the legislature. The president's degree of executive power may range from being reasonably significant (eg. Poland) to little or none at all (eg. Ireland). Where the president holds little executive power, their function is primarily that of a symbolic figurehead.
Mixed republican systems
Prime minister is also head of state and given title of president
Constitutional monarchies
Systems in which a prime minister is the active head of the executive branch of government and also leader of the legislature. The head of state is a constitutional monarch who only exercises his or her powers with the consent of the government, the people or their representatives.
|
Commonwealth realms
Constitutional monarchies, in which Queen Elizabeth II serves as head of state over an independent government. In each Realm, she acts as the monarch of that state, and is usually titled accordingly - for example, Queen of Australia. The Queen appoints a Governor-General to each country other than the United Kingdom to act as her representative. The prime minister is the active head of the executive branch of government and also leader of the legislature.
Semi-constitutional monarchies
The prime minister (or equivalent) is the nation's active executive, but the monarch still has considerable political powers that can be used at his/her own independent discretion.
Absolute monarchies
Monarchies in which the monarch is the active head of the executive branch and exercises all powers.
Theocracies
States based on a state religion where the head of state is selected by some form of religious hierarchy.
- Iran (to some degree)
- the Holy See (Vatican City)
One-party states
States in which political power is concentrated within a single political party whose operations are largely fused with the government hierarchy. However, some do have elected governments.
|
Military junta states
The nation's military control the organs of government and all high-ranking political executives are also members of the military hierarchy.
Transitional
States which have a system of government which is in transition or turmoil and cannot be accurately classified. (with current direction of change)
- Eritrea (presidential republic)
- Iraq (parliamentary republic)
- Nepal (constitutional monarchy or parliamentary republic)
- Somalia (semi-presidential republic)
- Sudan (bipartisan Government of National Unity)
- Thailand (constitutional monarchy)
Systems of Internal Governance
Federal
States in which the federal government shares power with semi-independent regional governments. In many cases, the central government is (in theory) a creation of the regional governments; a prime example is the United States.
|
|
Devolved
States in which the central government has delegated some of its powers to self-governing subsidiary governments, creating a de facto federation.
- Spain ( 17 autonomous communities and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla)
- United Kingdom (England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland)
Regionalized unitary
States in which the central government has delegated some of its powers to regional governments.
- Italy ( 20 regions, five granted 'autonomous' status)
- New Zealand ( 12 regions)
- People's Republic of China ( 22 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 municipalities, and 2 Special Administrative Regions)
- Philippines ( 17 regions, 1 granted 'autonomous' status)
Federacy
A federacy is a country in which some substates function like states in a federation and others like states in a unitary state.
- Denmark with 2 autonomous regions and 5 regions;
- Finland with 1 autonomous province and 19 regions;
- France with 1 sui generis collectivity and 26 régions, 4 collectivités d'outre-mer, 1 territoire d'outre-mer;
- Kingdom of the Netherlands with 2 states and 12 provinces;
- Portugal with 2 autonomous regions ( Azores and Madeira) and 18 districts;
- Serbia, significant autonomy granted to Vojvodina; Kosovo-Metohija under UN protectorate, future status being negotiated;
- Tanzania, 21 mainland regions, 5 regions under autonomous government of Zanzibar
- Ukraine, 24 oblasts, 2 special-status cities, and the Autonomous Republic of Crimea;
Unitary
see Unitary state
